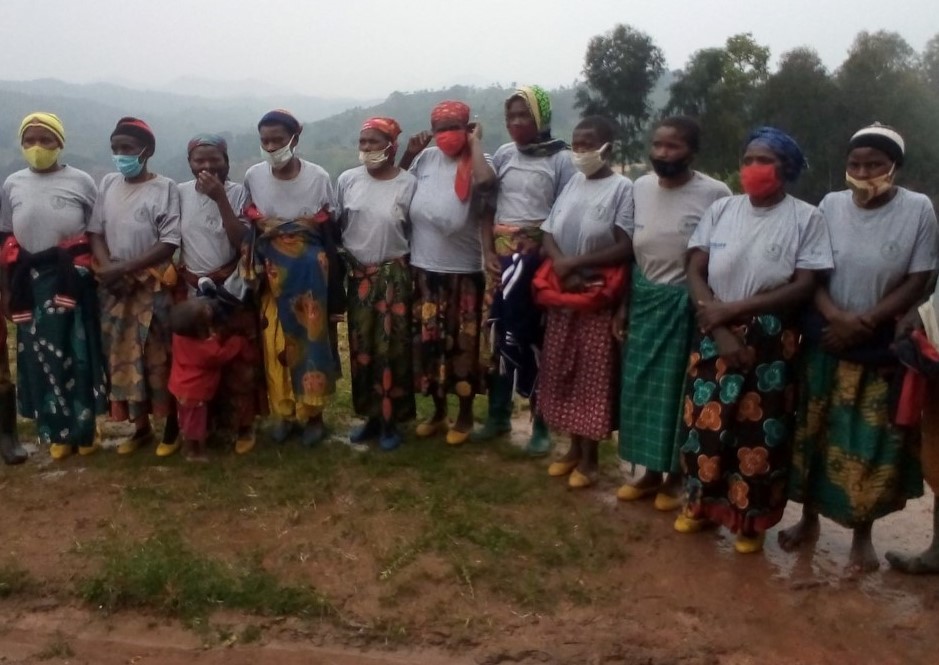
Rwandan women around Nyungwe National Park are running activities that are aimed at curbing animal poaching.
With 1,068 recorded plant species, 322 bird species, 75 known mammal species and 13 different primate species, the park provides 70 per cent of Rwanda’s freshwater and its value is estimated at $4.8 billion.
The women say they came up with the initiatives of fighting poaching in Nyungwe and its environs after understanding the importance of protecting the environment and the biodiversity species in protected areas. This is because they were receiving the harsher impacts of biodiversity degradation.
“When biodiversity is degraded, women are likely to face more effects than men due to their gender roles of looking for firewood, fetching water among other things,” 35-years-old Seraphine Nyandwi said.
Seraphine is among the women from Nyamagabe District in Southern Province who have embarked on protecting biodiversity species in the buffer zone of Nyungwe National Park and its environs considering that wildlife species live in the area.
The women said that they used to see their parents hunting for meat in the Nyungwe Forest, an activity that is currently illegal.
She said after her own initiative of understanding the importance of biodiversity, she realized the need to play a role in conservation.
“We are lacking information and knowledge on conservation. But as a woman, I have already understood the importance of biodiversity conservation and the fight against poaching, I also train members of the community including former poachers and they stopped the illegal activity,” she said.
She said that the former poachers are now playing role in sensitizing other community members to fight against poaching activities and participate in biodiversity conservation programmes.
Emmanuel Cyondi 55, who is a former wildlife poacher in Nyungwe National Park and its buffer zone stated that the women in the area explained to him how hunting is a threat to wildlife. “That is how I stopped poaching,” he stated.
“In Uwinkingi sector near the park, there are 15 women and 5 men who are committed to protecting the biodiversity species,” he added.
“These women are the ones who go around raising awareness about the importance of protecting the environment and biodiversity. Some of my neighbours already knew that I was hunting animals in Nyungwe and that is why they approached me and told me about the negative impact. I stopped poaching and will no longer hunt for animals,” he declared.
He said that it requires strategies to eliminate poaching in Nyungwe Park and its environs.
“In 2018, the women who decided to protect wildlife came to me at home and told me that what I was doing – hunting animals in the forest for meat was illegal,” he said.
He said that although it took time for him, he later changed to the extent of reporting other poachers who try to hunt in the park. “I alert local authorities and security organs so the hunters are arrested, prosecuted and punished by the law,” he noted.
Kevine Dusengimana, 26, is another woman committed to the conservation of biodiversity species. She says the community has to play a role in tracking down the poachers.
Most poached wild animals include deer, Kobs, The duiker (locally known as Ifumberi), l’hoest’s monkey (locally known as Icyondi) among others. “As women, we are determined to fight against poachers and we will continue to campaign in other parts of our country as we have understood that biodiversity plays an important role in our lives,” Ms Dusengimana added.
Challenges
The women stated that after realizing the importance of biodiversity conservation, they have joined efforts to form a group called UMURAVA, but they need support to gain capacity building in mobilising other Rwandans to participate in environmental conservation programmes.
Another obstacle that they face, is the attitude of some men whose wives take part in the conservation. “Such men say they will not benefit from it and rather force their wives to stay at home to fulfil their domestic responsibilities,” Pascasie Nyirampayimana, 42, another member of the group noted.
“Our husbands have a misconception about biodiversity conservation programmes because some do not understand the importance of conservation. Some say it is a waste of time, others say we go there for prostitution while others say it is a way of undermining men,” she said.
She stressed that such challenges are hampering their efforts in participating in conservation programmes. “Some women prefer to stop participating in conservation programmes so as to avoid conflicts with their husbands,” she noted.
These women say the community do not value them because of gender misconception surrounding what they do, men argue that conservation of biodiversity is not a source of income.
Solutions
Residents around the protected areas used to eat the meat of wild animals in the parks. Besides both men and women would go hunting for animals that are easy to catch such as quails and rabbits by using traps.
According to United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP), women can play an important role in the fight against poaching. This is because they can form environmental protection groups in their communities. With the groups, they can teach the community about conservation benefits and fighting poaching.
These women in groups will also help to change their husbands’ habits and stop poaching in the park.
In Rwanda country, gender balance has become part of the system, so local conservation experts are calling on women to ignore the cultural resistance and raise their voices in the fight against animal poaching. This way, people would eventually listen and they will help the local authorities to identify poachers.
The Chief Executive Officer of the Biodiversity Conservation Organization (BIOCOOR), Mr Ange Imanishimwe says he supports women in the conservation programmes despite the fact that some are yet to understand that they can benefit economically from biodiversity.
“The challenge affecting women’s participation in biodiversity programmes is that many people have not yet understood the importance of biodiversity, especially their husbands because they do not have enough information regarding the same. But we will help them to campaign and initiate talks with men so that they let their wives participate in this programme,” said Mr Imanishimwe.
The conservation expert also pointed out the need to engage men to support the participation of women in biodiversity conservation. This is because if the men understand and support efforts by women in biodiversity conservation, they would ensure that these measures will be accepted in the community. This inclusive approach would also tackle the root causes of gender inequalities. It would also create awareness thus resulting in long-term benefits for the whole community and the country.
What does the law say about poaching?
The amended law on biodiversity and wildlife has recommended strong measures against poachers and those who engage in the trafficking of wildlife as a way of protecting nature.
The law prescribes a prison sentence of between one and three years for a person convicted for poaching, injuring, taking, harassing or breeding a wild animal and a fine of between Rwf500,000 ($482) and Rwf1 million ($966).
If the offence is committed against critically endangered or endangered species, the penalty is a prison term of not less than five years but not more than 10 years and a fine of not less than Rwf5 million ($4820) but not more than Rwf10 million ($9706).
A person convicted for possession, transferring, selling, buying or using a wild animal is liable to imprisonment of not less than three years but not more than five years and a fine of not less than Rwf1 million ($966) but not more than Rwf5 million ($4820).
When the offence referred to is committed against critically endangered or endangered species, the penalty is between five and 10 years in prison and a fine of between Rwf5 million and Rwf10 million.
A person who takes or destroys eggs or nests of wild animals commits an offence. Upon conviction, he or she is liable to a term of imprisonment of between six months and two years and a fine of between Rwf500,000 and Rwf1 million.
In case this offence is committed against the eggs or nests of critically endangered species, and endangered species, the penalty goes up to between three and five years and a fine of between Rwf2 million and Rwf5 million.
According to the draft legislation, a person convicted for removing animal species from their habitat, harming, transporting, or hawking them is liable to a term of imprisonment of between six months and two years and a fine of not less than Rwf500,000, but not more than Rwf1 million.
In case it’s committed against endangered species, the jail time increased to between three and five years while the fine is between Rwf2 million and Rwf5 million.
The Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 15 is dedicated to “protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss” and indeed Rwandan women around Nyungwe National Park are not left behind.
This article is part of African Women in Media (AWiM)/UNEP Africa Environment Journalism Programme